The Evolution Of Virtual Reality

Introduction
Virtual reality is most widely utilized for entertainment, such as video games, 3D films, and virtual social worlds. Video game firms first introduced virtual reality headsets for consumers in the early to mid-1990s. Oculus (Rift), HTC (Vive), and Sony (PlayStation VR) all introduced next-generation commercial tethered headsets in the 2010s, igniting a new wave of application development. Sporting events, fine art, music videos, and short films have all utilized 3D cinema.
In this blog, we will be covering the following:
What is Virtual Reality?
The Origin
First Invention
- Virtual Reality in the 1950s and 1960s
- Virtual Reality in the 1970s and 1980
- Virtual Reality in the 1990s and 2000s
How does Virtual Reality work?
- Pros of Virtual Reality
- Cons of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality hardware and software
VR Devices
- Virtual Reality Headset
- Software
- Audio
Applications of Virtual Reality
- Healthcare
- Entertainment
- Automotive
- Education
- Space & Military
- Architecture
- Digital Marketing
- Occupational Safety
- Social Science and Psychology
- Tourism
Conclusion
What Is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality is a technique that mimics vision, resulting in a 3-dimensional environment where a person appears to be immersed through it or taking part in it. It is a 3D environment managed in 3D by the person in the experience.
On the other hand, the user making 3D VR environments experiences or explores them using appropriate devices like VR headsets. The use of computer technology to create a simulated environment that can dig in 360 degrees is known as Virtual Reality or VR. Virtual Reality, as compared to traditional interfaces, immerses the user in the virtual environment.
The Origin
In the previous 50 years, Virtual Reality has come a long way, yet it is still regarded as cutting-edge technology. It’s strange how it works. The detailed history that led to virtual reality’s existence is unknown; however, it has been a subject of discussion for many centuries. But, in the last few years, technology has risen to turn fantasy into reality.
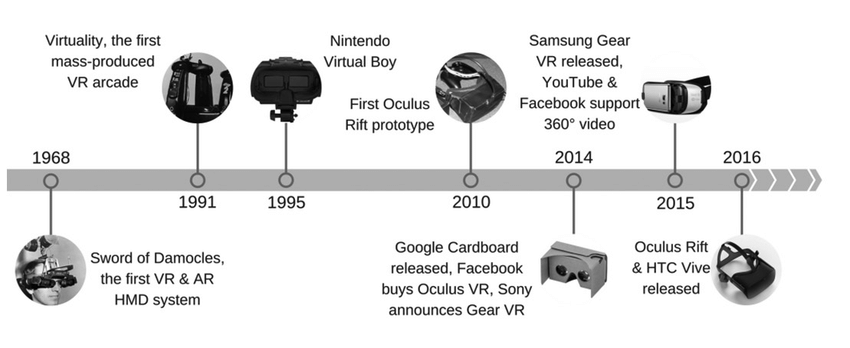
Image source: ResearchGate.com
First Invention
In 1968, American computer scientist Ivan Sutherland and his student Bob Sproull developed the first virtual reality headgear. While it was the first instance of a VR system that looked anything like we have today, ‘virtual reality had been proposed in art and literature since the 1860s.
To completely comprehend the development of this concept, we must first take a step back to discover how VR evolved from a mere hypothesis to a standalone reality.
Virtual Reality in the 1950s and 1960s:
Let’s look at the beginnings of this fictitious technology and how it came to be.
- The Sensorama, a theatrical cabinet multimedia gadget that allowed viewers an interactive experience, was designed by Morton Heilig, a cinematographer –1957.
- Comeau and Bryan, two Philco Corporation engineers, designed the Headlight, the first head-mounted display (HMD) – 1961
- A military engineer named Thomas Furness created the first flight simulator for the Air Force –1966
- Ivan Sutherland, a Harvard professor, and computer scientist, developed ‘The Sword of Damocles,’ the first VR/AR head-mounted display -1968
Virtual Reality in the 1970s and 1980s:
- The Aspen Movie Map, created by MIT, utilizes images taken from a car in Aspen, Colorado, to provide viewers with a “Surrogate Travel” experience –1978
- The film Tron popularized the concept of Virtual Reality –1982
- The phrase ‘virtual Reality’ was coined by John Lanier, a computer scientist, researcher, and artist. He founded the Visual Programming Lab (VPL) and co-developed Dataglove –1987
Virtual Reality in the 1990s and 2000s:
- The Virtuality Group produced a series of games and arcade machines, making Virtual Reality accessible to the general public –1991
- Nintendo released the Virtual Boy, the first portable system with 3-D graphics – 1995
- The SAS cube was the first PC-based cubic room introduced. The Virtools VRPack was born from the SAS library – in
- Google announced Street View in collaboration with Immersive Media –
How Does Virtual Reality Work?
Virtual Reality technology permits the creation of a digital environment aimed at replicating real-world scenarios or creating an imaginary world made up of non-realistic components, for example, games that allow players to participate in different methods with risk-free options.
Virtual Reality is a complete immersion of the user in virtual reality. For these experiences, the user requires VR headsets to experience the entire 360-degree understanding of the virtual world. It’s a preferred technology in the entertainment and gaming industries and is entering other sectors, including construction and medical.
Pros of Virtual Reality
- It creates an engaging learning area; students can practice their abilities with VR. For instance, medical students could practice performing surgery instead of looking through AR.
- Improved cognitive abilities VR could aid the user in developing their thinking and decision-making abilities. A new pilot may wish to go through a risky scenario in a virtual world to gain experience and prepare for what is likely to occur within the actual world.
- Improved social interaction: In the wake of events that will cancel around the globe in 2020 and 2021, VR programmers have developed a place where users can live stream the event from the virtual space. It makes people feel as if everyone is in the same area.
Cons of Virtual Reality
- Addiction: Similar to AR, it is possible to run the possibility of addiction among VR users. It is precarious since users are involved in illicit activities in real life, which they can now transfer to the world of Reality.
- User’s health: There are a variety of effects on the user’s health. There is a possibil
ity that VR can cause loss of awareness and dizziness, disorientation, confusion, and nausea. - Loss of connections: This may occur when users depend on VR for social interactions, as they prefer to do it in real-time.
Virtual Reality Hardware And Software
We’ll learn about the VR hardware and software that makes Virtual Reality possible, the specifics of virtual reality headsets, and how they work.
Hardware
VR hardware can be employed to generate stimuli to control the sensors of the VR user. They can wear on the body or in isolation from the user. VR hardware utilizes sensors to monitor motions, for instance, the user’s button presses and the controller’s movements, such as hands, head, or eyes. Sensors have receptors that capture the energy generated by the user’s body.
The sensors within the hardware convert the energy it receives from hand movements or button press into the form of an electric signal. The signal is transmitted to the device or computer for the appropriate action.
VR devices
- There are hardware devices that enable VR technology. They are personal computers that can process outputs and inputs from users and phones, consoles, and consoles.
- Input devices: It includes VR controllers balls or the tracking ball, controller wands trackpads, data gloves, buttons for controlling devices bodysuits, motion trackers motion platforms, and treadmills (virtual Omni) that employ pressure or pressure to create energy which is then converted into an electrical signal that allows the user’s selection possible in a 3D environment. These devices help users navigate through the 3D worlds.
- The computer should be capable of rendering high-quality images and typically employs Graphics Processing Units to provide the highest quality and user experience. Graphics Processing Unit or Graphics Processing Unit is an electronic device in a card that receives information from the CPU and alters and manipulates memory to speed up creating images within the frame buffer and the display.
- Output devices include the auditory and visual or haptic displays that stimulate the senses and display the VR contents or the environment to users to create an experience.
Virtual Reality Headset
VR headsets are head-mounted devices that can offer virtual reality images for the eye. A VR headset comprises a visible screen or display lenses and headphones, stereo audio, or eye motion cameras or sensors to the same effect. Sometimes, it also includes controllers integrated or connected, which are used to navigate through VR content.
Image source: dazeinfo.com
- The sensors that detect the head or eye movement and track it could comprise gyroscopes, structured lighting systems, magnetometers, and accelerometers. Sensors are used to decrease the load on rendering and deliver ads for advertisement. For example, in reducing the burden, the sensors are utilized to determine the user’s gaze and reduce rendering resolution to the user’s eye.
- Image clarity is determined not only by the quality of the camera but also by the resolution of the display optic quality, refresh rate, and area of vision. Cameras also monitor motion, for example, to create room-scale VR experiences in which the user can move around a room while experiencing virtual real-world. But, sensors are more efficient as cameras typically have a more significant delay.
- With P.C. Tethering VR headsets, the ability to move freely around while you explore VR surroundings is a significant problem. Outside-in and inside-out tracking refer to two different terms commonly used in VR. Both terms refer to how the VR system can track the user’s location and any accompanying devices when they move about the room.
- The VR headsets are usually mid-range, low-end, and high-end VR headsets. The lower end includes the cardboards utilized in conjunction with mobile devices. The mid-range range includes devices like Samsung HTC Vive, a mobile headset with a dedicated portable computer, and PlayStation VR. Lastly, top-end models consist of P.C.-tethered and wireless headsets such as HTC Vive, Valve, and Oculus Rift.
Software
- Controls the VR input and output devices, analyzes the input data and generates the correct feedback. All input for VR software must be in sync, and its output must be swift.
- The VR developer can create their very own Virtual World Generator (VWG) by using the software development kit provided by a VR headset manufacturer. An SDK includes primary drivers that allow access to the tracking information and call graphics rendering libraries. VWG can be customized for specific VR experiences.
- VR software relays VR content stored in Cloud and different sources through the Internet and assists in managing the content.
Audio
Some headsets have the headsets with their audio systems. Some headsets allow using headphones as an add-on. Virtual reality audio is a 3D illusion for the ear that can be created using a multi-speaker with a positional feature commonly referred to as positional audio. It gives the user clues to draw their attention or give the user some details.
This technology is now used in surround audio systems.
Applications Of Virtual Reality
Healthcare
The primary method VR modernizes healthcare is through education. VR creates a place that allows you to grow and learn from the classroom in real-world settings.
With VR, professionals who must perform precise operations can train without being in the middle during an emergency.
Practitioners who want to become familiar with the hospital’s environment can do this without stress.
This technology is used in cognitive behavioral therapy, where people suffering from anxiety or phobias work on their issues in a controlled space.
Entertainment
The entertainment sector was among the first industries to adopt VR and is still one of the best examples of its use. If you examine gaming on consoles and online, it will be apparent that VR has a significant presence in the gaming industry.
Similar to VR, HTML0 is now being introduced to theme parks and cinemas to recreate movie-like experiences and allow people to enjoy their favorite cinematographic works.
Automotive
VR assists car makers in analyzing road situations and the behavior of cars. Simulations allow the users to study and alter the models before constructing the next model.
Virtual reality is widely utilized in creating smart cars that will be flooding with new models in the coming years. Autos learn to drive, turn, and stop using AI (AR) and virtual reality.
Education
Although education is thought to be a slow business to adopt the latest trends and technologies, VR has already shown the potential of VR.
For adults, any business offers professional education to its employees. VR is a component of games for education and field trips and generally experiencing the world for younger students.
Space & Military
Because these two sectors must operate in hazardous environments that aren’t accessible, VR provides conditions for getting like reality feasible for training.
VR lets trainees prepare for their training with minimal risks. It also assists those who have suffered from trauma on the battlefield to overco
me their injuries and prepare for unexpected scenarios.
Architecture
With VR architecture, architects can visualize what they are designing and what it feels. It lets them feel the space before its construction and implement real-time adjustments to provide the best customer experience.
Digital Marketing
Though most people aren’t a fan of commercials, the experience of a close-up view of a product can be fun and educational. There are numerous uses for VR in the realm of digital marketing.
For instance, retailers could explain what the product will look like at home to prospective customers. Nonprofits can also create more humane messages to address politics.
Occupational Safety
Safety and health at work (OSH) can be a significant concern for any workplace with machines or natural dangers.
The workplace hazards can be dealt with through a simulation environment where employees can be taught how to handle them without causing injury.
Social Science and Psychology
The majority of the industry is based on VR so that users can imagine themselves as another person and experience the world from a different angle or perspective. Immersive environments have positive effects on future interactions between people.
Tourism
Take a trip before you purchase it. No, seriously. One of the most popular virtual reality applications is tourism. You can take virtual tour tours through the hotels, landmarks, restaurants, and anything else you’d like to see during your next trip. If you decide to go, you’ll be sure that you’ll be impressed.
Conclusion
This comprehensive virtual reality article introduces you to the concept of the evolution of Virtual Reality, commonly known as VR. We also learned how lenses for the headset work with the eye by using light emitted in and out of sight, creating these visual illusions.
In this context, we also looked at the factors that impact the quality of experience provided by VR for the viewer and how it can improve. We also explored the various applications of VR, which included gaming and training.




