Blog Post
The Future of Healthcare Apps

Introduction
Think apps are just for fun? Think again. Healthcare apps are big news and are getting a lot of attention as mobile technology becomes cheaper and more accessible to the everyday person. There are new apps being created every single day that are meant to help improve the quality of healthcare and reduce the cost of treatment. This guide will help you properly understand what is coming down the pipeline in the mHealth sector and how it might affect a physician’s practice and patient’s wellbeing journey.
This blog post covers the following information:
- Understanding Mobile Health Technology (mHealth)
- Types of Healthcare Applications
- Predicting The Future of Healthcare Apps
- Some Famous Healthcare Apps
- Monetization of Healthcare Apps
- Conclusion
Understanding Mobile Health Technology (mHealth)
Mobile health, or mHealth, is a broad term that describes the use of mobile devices to gain access to healthcare information, manage and improve health behavior, and improve the delivery of healthcare services. Mobile health devices can range from smartphones and tablets to wearable devices, such as activity trackers. The technology also includes mobile phones that are modified for healthcare purposes.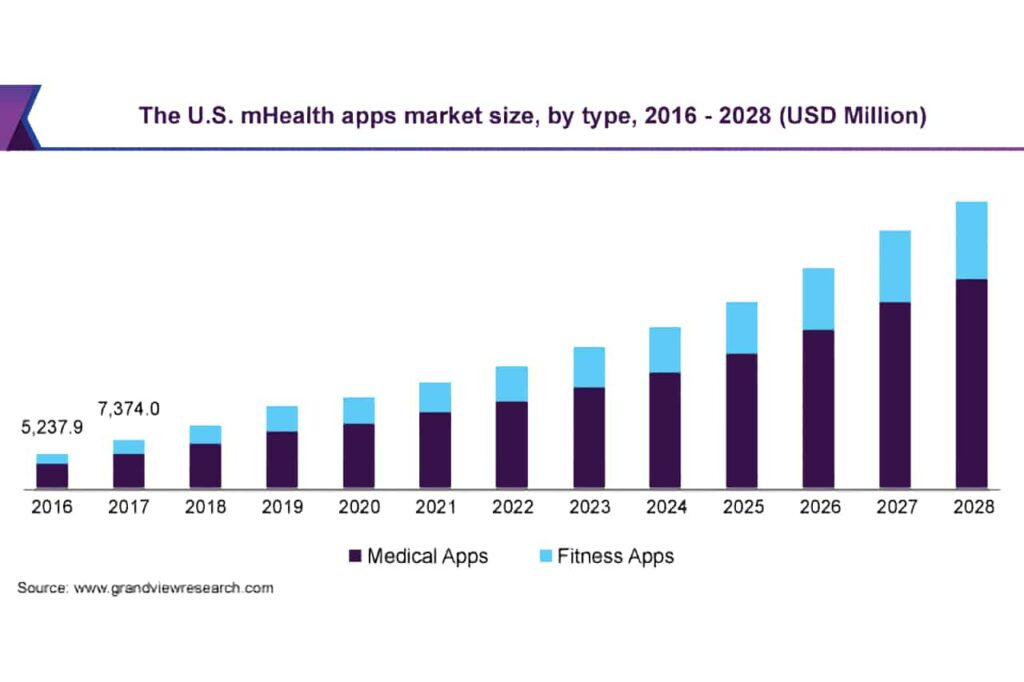
A graph showing a surge in mHealth market size and share (2016-2028) Source
According to insights, the global mHealth market size valued at around USD 56 billion in 2020, will grow at over 30% CAGR from 2021 to 2030. Healthcare apps are a key part of this technology. For example, if you have diabetes and use a cell phone app to help you monitor your blood sugar levels throughout the day, you’re using mHealth technology!
By the end of 2021, there are 320,000 mHealth apps available on the Internet. These apps require people to input large amounts of data manually. Some of these apps have artificial intelligence (AI) functionality that can help detect early signs of disease by analyzing collected data.
According to research, the most common uses for mHealth apps include:
● Health and chronic disease management (41%)
● Monitoring wellness (20%)
● Tracking fitness (18%)
Types of Healthcare Applications
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines mobile health (mHealth) as “medical and public health practice supported by mobile devices, such as mobile phones, patient monitoring devices, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and other wireless devices.”
Mobile health apps fall into three main categories:
● Apps that are used to monitor the health
● Apps that are used to manage or treat a particular condition
● Apps that aim to promote general health
There are many different types of mobile health apps, which are categorized based on their primary goal or function. Some common types of mobile apps include:
Diagnostic Applications
Diagnostic applications are the most popular category of mHealth apps, with a market penetration of 31%. The reason for their popularity is that users can self-diagnose medical conditions, which often means they don’t have to pay a visit to the doctor. (They can always make an appointment, but at least they’ll know what to ask about and how worried to be.)
There are two main types of diagnostic apps: symptom checkers and disease management apps. Symptom checkers are usually free and are designed to help users figure out what’s wrong with them based on the symptoms they’re experiencing. Disease management apps like Flaredown are essentially tracking tools for people living with long-term illnesses like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. They help users monitor their health on a regular basis and track progress in managing their condition.
Monitoring Applications
Also called data collection apps, these are typically apps that track things like your daily calories burned or consumed, your moods over time, or how often you brush your teeth. They can also include things like reminder notifications if your doctor has suggested that you take regular medication throughout the day or have scheduled appointments coming up. These monitoring apps allow you to quickly see trends in your diet or exercise habits so that you can make changes accordingly.
Health monitoring apps like Instant Heart Rate provide real-time data about things like blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, and sleep; in some cases, monitoring apps are integrated with medical devices and offer a continuous stream of biometric data (e.g., blood pressure monitors).
Information Applications
An information application is a mobile health application that provides the user with information only. These apps don’t record or track any data, but rather just provide information to users in order to help them better understand their health or a certain condition. These types of apps are most useful when they are provided by an expert source (such as a government agency).
Several examples of these apps include:
● Apps that tell you how many calories are in the food you’re about to eat
● Apps that teach you how to do specific yoga poses
Intervention Applications
Intervention applications help users understand what they can do to change certain behaviors or habits. For example, a smoking cessation app might offer tips for how to quit smoking, as well as reminders to not smoke and help with stress management.
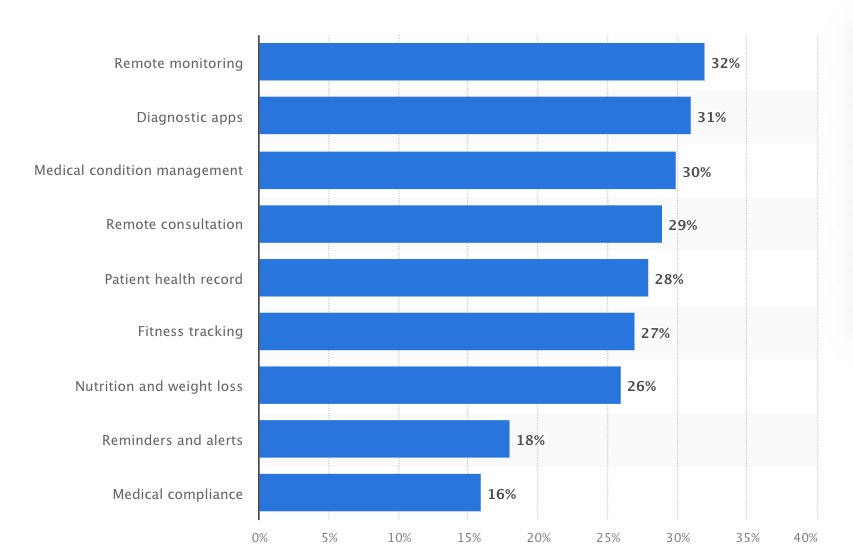
A chart showing Healthcare App categories with the highest global market potential (2016-2022) Source
Predicting The Future of Healthcare Apps
The future of healthcare apps is now. Information has always been the lifeblood of medicine, and the Internet has enabled an explosion in medical information. Today’s healthcare apps allow busy doctors to access real-time patient data from anywhere, helping them ensure that patients are receiving quality care at all times.
These applications are growing in number, and the future is promising for both patients and healthcare mobile app design and development consultants.
According to insights from eMarketer, about 30% of adult smartphone owners in the United States used a health or fitness app monthly in 2020—that’s about 87 million people. This number is expected to remain relatively stable in the next three years.
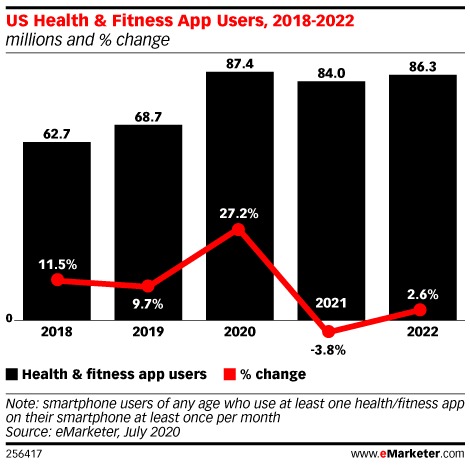
A graph showing the trends of Healthcare Apps in USA (2018-2022) [source]
The future of healthcare apps will ultimately depend on how well, apps can respond to the patient’s needs.
BUT…
Do we have some amazing technology that can help fill the healthcare gap in the coming years? Let’s gain some insights into where medical apps are heading.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is getting better than ever at diagnosing medical conditions. It can identify patterns in medical data and then diagnose patients based on those patterns—which makes it an incredibly powerful resource for physicians. AI is likely to be particularly useful when working with a high volume of patients, as the potential for error usually increases as the number of interactions increases. AI could help physicians avoid making mistakes and keep patients safe.
Patients should also benefit from AI in the future of healthcare applications. One example of this is natural language processing (NLP). In NLP, systems are designed to analyze, understand, and extract information from human speech. This is exactly what IBM’s Watson Health does: a doctor can ask Watson questions about a patient’s symptoms or condition, and Watson will be able to give them rapid feedback based on the information he has been fed through his database of journals and studies. This can save doctors precious time while they’re trying to give patients the care they need.
Think of going to the nearby clinic, where you are greeted by a little machine that takes your blood pressure and gives a preliminary diagnosis. You only see the doctor if there is something unusual about the results. When you think about it, this makes perfect sense. That said, there are more advanced applications of artificial intelligence in medicine on the horizon. According to health care experts, AI will soon be able to:
● Predict cancer risks
● Prescribe medication (not just tell you what you should take)
● Diagnose illness using images and symptoms
An example of AI in action:
Let’s assume you’re running a fever, but have no idea why. You head to your doctor’s office, and before you even know what’s happening, your nurse tells you that she’s tested you for the flu and strep throat, and has already sent off a blood sample to be analyzed for a number of other potential illnesses. You ask her how she knew to test you for all of those things, and she tells you that it’s because of your medical history (which is all contained in your patient record) and symptoms that are stored in your iPhone app.
This is just one example of how AI is making healthcare more efficient: by helping doctors identify the right tests to order based on patient data that has already been collected. The next step will be training AI agents to make personalized recommendations based on similar patients’ health histories and diagnoses. Imagine telling your phone about your symptoms—and having it tell you what kind of medication might help!
Blockchains
Since the coronavirus pandemic began, there have been more than 40 million patient records compromised in incidents reported to the federal government in 2021. Many healthcare providers are unprepared for the changing threat landscape and increasing sophistication of hackers, leaving their patient data at risk of being compromised.
Therefore…
Blockchains are going to play a major role in the future of healthcare apps. They are already being used for functions like maintaining and verifying medical records, and we have only just scratched the surface of their potential.
One of the great benefits that blockchains will provide is more thorough data analysis and better recordkeeping. Blockchains allow for speedy, secure data collection from across many different sources, leading to more comprehensive patient histories. This can not only help with treatment decisions but also with developing new medical technology by analyzing trends across large datasets.
The other boon offered by blockchains is secure data sharing. Medical records are some of the most sensitive information out there, and making sure that they are protected is crucial. Blockchains offer a secure way to share records across multiple providers while preventing users from improperly accessing or modifying them without proper permissions.
This kind of security will be especially important as telehealth grows in popularity. Telehealth allows patients to receive care remotely using apps or video chat services, and its growing popularity means that it’s more important than ever to ensure that patient records remain private and properly secured.
VR/AR
Virtual and augmented reality technology will be used in healthcare apps to provide a better patient experience, increase compliance with treatment, and improve patient outcomes. It will also give doctors more insight into their patients’ health. There are several interesting ways VR/AR technology will be used in healthcare apps.
Creating Content That Fosters Greater Understanding
A patient can use an augmented reality app to get a first-person look at what is happening inside their body while they undergo a procedure. The doctor can also use the app to explain what is happening during the operation and why it needs to be done. By using an augmented reality app, patients can feel more informed about their health and be more involved in their treatment decisions.
Advanced Visual Systems Helps Train Surgeons
Virtual and augmented reality technology is also useful for training doctors and nurses. With simulated scenarios, students can get hands-on experience without putting themselves or real patients at risk of making mistakes. They can learn how to treat different conditions and perform procedures without having to practice on real patients until they have mastered the skills needed for the job.
A Tool For Patient Entertainment
One of the most well-known uses of VR is its ability to help patients “escape” from the discomfort or anxiety of their current situation by immersing them in a completely different world.
For example, if someone is undergoing radiation therapy, they would typically be laying in one spot for an extended period while a machine moved around them, blasting them with radiation. Now, a VR app could put the patient “inside” their favorite movie or on a beach in Tahiti, making the process much less unpleasant for the patient. There are many other ways VR can be used by healthcare companies; some of these include surgical simulations, visual aids for doctors and patients to communicate more effectively, and even helping with prescriptions.
Allowing Patients To See Results And Changes On Screen
It helps patients visualize their conditions. For example, if you have multiple sclerosis, you can use VR to see what your brain looks like now, and what it would look like if you do not get treatment. Research shows that patients are more likely to take action when they can visualize the benefits of doing so.
Another example is, if you’re receiving chemotherapy treatments, there are VR apps that help you visualize your body becoming healthy again and provide other positive imagery to encourage you through the process.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine will be the future of healthcare applications. In fact, the market for telemedicine—or virtual consultations—is expected to reach $186.5bn by 2026.
Modality Systems’ OneConsultation (a telemedicine software) has been hosting virtual consultations for over three years and has hosted over 100,000 calls in 2021, with an average of 832 calls a day with the NHS alone!
More and more people are having access to smartphones and doctors can easily connect with their clients through this medium. This is particularly useful for doctors who are based in remote areas where it is difficult to see patients in person. These doctors can see the patient via teleconference or video call, which is a huge boon for those who do not have easy access to a telephone or reliable internet connection. Also, if you’re stuck at home, this would be much more convenient than having to take time off work to travel all the way into town just so that you can visit your doctor’s office!
The best part about telemedicine is that it will allow patients to have more control over their own health care decisions by providing them with access to medical information whenever they need it. In addition, this type of technology has potential benefits for those who live in rural areas where there may not be enough physicians available locally. This means that people will be able to get treatment from specialists without having to leave their homes or take time away from work because they’re traveling hundreds of miles just so they can see someone in person!
Internet of Things (IoT)
With the advent of the Internet of Things or IoT, our lives have become easier than ever before. IoT is basically a network of devices that are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other. This new technology has ushered in a new era of convenience, permeating almost all of our daily activities—including healthcare.
Here’s how it works: sensors embedded in medical equipment measure your vitals and send alerts that are processed by your personal assistant, which alerts you to potential problems. This equipment can also be used to monitor patients who may be at risk for health issues or elderly patients who live alone.
In addition, IoT integration has also made it possible for doctors to monitor their patients remotely and collect data about their experience with treatment. While this may seem like just a cool new way for doctors to keep track of you, it actually has serious implications for patient care. For instance, if a doctor knows what kinds of questions his patient has asked while using his app, he will know exactly what’s on her mind when she comes in for an appointment—and that information can help him better manage her condition.
All of this will be done using wearable devices that are connected with the hospital management system.
For example: Take a patient who has an issue related to blood pressure. He visits a doctor and after proper analysis, the doctor prescribes medicines to control blood pressure. The patient wears a smart band while going home. The band has sensors that can measure blood pressure and send data directly to the hospital management system. If there are any issues in controlling blood pressure then the hospital staff will automatically get notified regarding this issue. They will contact the patient and ask him/her to visit again or give instructions over phone call according to issue severity.
Some Famous Healthcare Apps
These are some health care apps that are currently operational an
d making their way into the market. However, we might only be looking at the tip of the iceberg as more and more advanced health care apps will be coming out with more sophisticated technologies in the future.
Doctor on Demand
Doctor on Demand is an online platform that allows patients to consult with healthcare providers via video chat directly from their phones. It’s based in San Francisco, California, and boasts $74 million in funding and nearly $12 million in annual revenue.
2nd.MD
2nd.MD is an online platform that lets patients consult with healthcare providers. This is great when you have a non-emergency health issue, as well as if you want to get a second opinion on your diagnosis or treatment plan. This app was founded in 2011 but has still managed to attract $2.29 million in investment just last year—a testament to its success and popularity among users.
Amwell
Amwell is an online platform that lets you have on-demand video visits with doctors who can diagnose and treat many common ailments. It’s supported by American Well, which has been in the telehealth business for more than a decade and has worked with top healthcare providers across the country. Amwell is dedicated to making it easier for people to get quality health care without having to deal with long wait times and congested waiting rooms. Amwell doctors are available 24/7, 365 days a year, and in some areas, patients can even get prescriptions delivered straight to their door.
Monetization of Healthcare Apps
The healthcare industry is in the midst of a digital transformation that has left many wondering how to translate their efforts into revenue. You may be familiar with the various monetization methods that have been implemented by companies of all sizes, but you may also be asking: “How will we be able to monetize our digital presence?”
This is a burning question that we are asked frequently, so let’s take a closer look at some of the most popular ways to monetize your healthcare app.
In-App Ads
Monetize your mHealth app with in-app ads. Just like you can make a living off of your blog or YouTube channel, you can make money from your mobile health app by incorporating ads into the app experience. The trick is to not let the ads feel like an intrusion into the user’s health-seeking experience. Instead, think of it as a natural extension of the kind of content that would appear on a website: relevant, engaging, and sometimes funny.
In-App Purchases
You can put certain features behind a paywall. For example, if you have a meditation app, you could have one type of meditation be free and another type cost money. Or maybe you have an app that helps people with anxiety and one of the features is a subscription to get daily affirmations via text message. This would be a great place to put a paywall because it’s something that users would really value and use every day.
Selling Information
If your mHealth app helps people track their mental health, you could sell their data to other companies or research institutions that are interested in the data. However, this is only ethical if you get the user’s consent beforehand!
Subscriptions
This is when your users pay a regular amount of money to access specific features of your app. For example, they might pay as little as 99 cents a week to use all the features in your app, or they might pay $10 a month for unlimited access to only one feature.
Some examples of apps that use this model include: fitness training apps like Map My Fitness, meditation and mental health apps like Calm, and sleep tracking apps like Sleep Cycle.
In order to make this work for you, you have to have a great product (obviously), a loyal customer base that keeps coming back for more of your awesome product, and a service that can’t be rendered obsolete by anything else on the market.
Freemium Model
If you offer a basic app for free and charge for more advanced features like additional content or in-app purchases, then your users may be more likely to upgrade and pay for premium content. For example, fitness apps can offer a premium service with personalized workout plans from certified trainers.
Sponsorship Deals
Offering sponsorship deals provides another means of monetizing mHealth apps. This works best if you have a large number of users who will see the sponsored content within your app, which increases engagement and exposure to the sponsor’s brand or product.
Partnership with healthcare organizations
There are many healthcare organizations looking to use technology to reach out to as many patients as possible. You can partner with these organizations and allow them to promote their services within your app for money.
Best Technology Solutions for Building Future Healthcare Apps
Software and mobile device technologies are now enhancing day to day operations in the healthcare industry in ways which were not possible a decade ago. The use of these technologies are radically changing the face of the healthcare industry. It has become essential for physicians, doctors and surgeons as well as others associated with the medical industry to be aware about these technologies. Also, with new laws such as HIPAA reforms, there has been an increased awareness of patient data security; hence a more secure system is now required.
Drupal
Drupal is the only technology that provides a healthcare experience that complies with HIPAA standards. HIPAA compliance requires strict adherence to privacy and security regulations, and Drupal provides built-in functions that make meeting these requirements simple.
With Drupal, your website can be configured to hold information in such a way that it can’t be lost, stolen, or shared without authorization—and if you do need to share data, you can make sure it’s done securely.
Additionally, Drupal has a strong community of developers who are familiar with the unique needs of healthcare applications and websites, including the specific requirements of HIPAA compliance.
|
What makes Drupal the right choice for future healthcare applications? Secure: Drupal is a secure platform that allows healthcare websites to remain protected from hackers and cyberattacks. Com Robust: Drupal’s robust framework offers a variety of add-ons, plugins, and other tools so that healthcare websites have the ability to continually evolve to meet the needs of patients, providers, payors, and other stakeholders. |
Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS)
With BaaS, the patient is always at the center of care. With BaaS, you can easily develop applications that will help put you at the forefront of technology in the field of healthcare.
By using BaaS to create applications for your healthcare organization, you’re giving your patients a way to access their data anywhere and at any time. You’re also giving them a way to communicate directly with their providers and engage in their care plans. And as an added bonus, you’ll be able to use real-time data collection to improve your treatments.
According to healthcare media experts like HIT INFRASTRUCTURE, “EHR integration can be complex and costly, making it hard to deploy an App. BaaS can cut costs and smooth the process.”
BaaS takes care of all of your server-side needs: creating databases, storing data, and setting up push notifications. This makes it the perfect technology for creating solutions that rely on data storage, like those in the healthcare industry.
For example, when creating an application for managing patient information and records, it is essential to have a reliable database that can be accessed and updated by multiple users without causing any issues (like duplicate records). By using BaaS instead of building your own backend from scratch, you are guaranteed to have everything set up correctly—and you won’t waste your time coding something that already exists.
Low Code Development Platforms (LCDP)
Low-code platforms can help healthcare organizations develop and deploy applications faster, meet new compliance requirements, and enhance the capabilities of their existing applications. Low-code platforms combine a visual development environment with pre-built components, connectors, and templates so that business users can easily create applications that cut across many different functions or departments.
By using low-code tools, organizations can accelerate application development and dramatically reduce the time it takes to build and deploy an app. IT staff can use low-code tools to quickly build apps for internal operations and then rapidly configure those apps for external clients or patients.
And when regulations change, healthcare organizations can use low-code tools to quickly modify applications to meet new requirements. With the drag-and-drop interface of a low-code platform, developers can make changes or add new features in a fraction of the time it would normally take with traditional coding methods.
Because they work with existing systems and data sources, low-code platforms reduce complexity, eliminate the need for wholesale system replacements, and make it easy to integrate other technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotic process automation (RPA), and blockchain into your development projects.
Conclusion
With the surge of apps in the healthcare sector and the increasing use of smartphones among younger generations, the evolution and adoption of healthcare-related apps will most likely continue. More people all over the world will be able to benefit from easy access to vital health information, all at their fingertips. This is an exciting opportunity and one that both patients and healthcare services would greatly benefit from exploring further.
We at MpireSolutions are a leading app developer that provides high-end technology solutions to individuals, small and large medical firms in the US. We have successfully developed and deployed a number of successful healthcare applications for health businesses. Please contact us for more information on how we can help you with your Healthcare applications and softwares.




