Blog Post
Here’s Why Cloud Computing is the Future!

Cloud computing is the latest trend in information technology. If you want to be ahead of your competition, it’s time for a change.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing allows businesses and organizations to avoid making major investments by renting services over the internet rather than buying them outright or leasing physical space on servers. These cloud-based service providers are divided into three categories: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Services (SaaS).
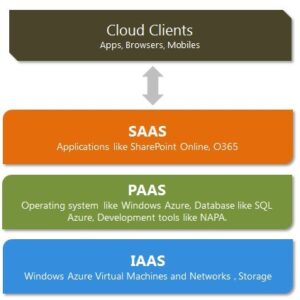
A cloud can be public or private. A public cloud sells services to anyone over the internet, while a private one is restricted by only hosting data for those in its network with specific permissions and access levels. The goal is always the same though – easy, scalable access to IT services and computing resources.
The Internet is often represented by a cloud in diagrams and flowcharts, and the name “cloud computing” was inspired from this. Cloud computing is a relatively new concept that continues to grow in popularity as the technology behind it improves.
Using cloud infrastructure can save time and money when compared with on-site data servers, while also providing an always available solution for accessing needed resources at any given moment via internet connection.

How does “Cloud Computing” work?
Cloud computing is an innovative technology that allows people to access data remotely over the internet. It works by allowing clients devices to connect with remote servers, databases and computers through an internet network connection. The back-end of this system comprises mainly of computer systems and databases which store all necessary information for front-end programs like browsers or apps on your phone.
A central server manages communication between the back end and front end. The exchange of data is facilitated by protocols which ensure security for users’ information. Software, middleware, and dedicated servers are all used to facilitate connectivity with different client devices as well as cloud servers on the internet.
Examples of Cloud Computing
Here are some notable examples of cloud computing:
Zoom: Zoom is a phenomenal software application for audio and video conferencing that comes in handy when you need to record your meetings or conduct remote webinars. It’s accessible on any device with an internet connection, so all of the information you save will be available on demand anytime!
AWS Lambda: Lambda is a cloud service that allows developers to run code for applications or back-end services without the need of provisioning and managing servers. The pay-as-you-go model scales with the organization, allowing them to accommodate real-time changes in data usage and storage needs.
Google Docs, Microsoft Office 365: Users can access their work presentations and spreadsheets anytime, anywhere on any device by signing into Google Docs or Office 365 through an internet connection.
Email, Calendar, Skype, WhatsApp: Emails, calendars, Skype and WhatsApp utilize the cloud’s ability to grant users remote access to data so they can be productive from anywhere, and at any time.
Cloud computing vs. Traditional web hosting
Cloud computing has three characteristics that distinguish it from traditional web hosting:
- Cloud users can access large amounts of computational power on demand, eliminating the need to purchase and manage their own servers or data centers.
- It’s an elastic service which means the user only pays for as much as they need at any given time; there are no overages for going over allotted usage limits from one month to another like with traditional web hosting services.
- The provider manages everything including security updates and maintenance – all you have to do is sign up! Cloud computer innovations such as virtualization along with advances in internet speeds have made this type of technology more popular than ever before!
Features of Cloud Computing
Some of the main features of cloud computing are:
Self-service provisioning: End users can now effortlessly spin up computing capabilities at the click of a button. Gone are the days where IT needed to provision and manage all those resources, giving end-users more freedom over their workflow!
Elasticity: Computing demands are constantly in flux. The ability to scale up and down is an excellent way for companies to address this fluctuation without the need for large investments in local infrastructure that may or may not remain functional.
Pay per use: The user pays only for what they need and use, instead of paying a set fee. This means it could be more affordable to buy additional resources when necessary instead of purchasing multiple licenses upfront in order to have enough resources later on.
Workload resilience: Cloud service providers tend to implement redundant resources to ensure resilient storage and keep their users’ essential workloads running smoothly, with backups in multiple regions worldwide.
Migration flexibility: Organizations can move specific workloads to or from the cloud — and even between different cloud platforms as desired. This helps organizations save time and money, while allowing them to take advantage of the latest services and emerging technologies.
Broad network access: A user can access cloud data and upload data to the cloud from any device and location over the internet.
Multi-tenancy and resource pooling: Multi-tenancy is where multiple customers share the same physical infrastructures or the same applications, while retaining privacy and security over their own data via special permissions or restrictions. These pools tend to be very large and flexible enough to effectively satisfy changing customer needs.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing boasts many attractive benefits for organizations and end users. Some of the major benefits of cloud computing are:
Cost-efficiency: With cloud infrastructure, organizations don’t have to invest large sums on purchasing and maintaining equipment which significantly reduces their capital expenditure – they don’t need large IT teams either because all that work is handled by experts on the cloud provider’s team. Cloud computing also cuts down on downtime related expenses thanks to quick access times and built in redundancy features like backups for data storage facilities or power grids.
Mobility: Cloud computing means that people can access their files from anywhere with any internet-connected device. This saves users the hassle of carrying around USB drives, external hard drives or CDs to get what they need for work. It also allows remote employees stay up to date on co-workers and customers in order to perform at a high level. And because vendors provide upgrades automatically, end users save time by not having to worry about updates themselves!
Disaster recovery: No organization is safe from data loss. But storing it in the cloud protects users against all sorts of unexpected events, such as natural disasters or power outages. Organizations can quickly recover their data by hopping on to a different device and logging into the same account!
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a great alternative to traditional server systems, but it does pose its own challenges for IT professionals:
- Cloud security: Cloud security is often considered the greatest challenge facing cloud computing, and with good reason. When customers rely on the cloud for data storage and computing power, they risk having their sensitive information breached by hackers or being leaked when credentials are compromised.
- Lack of transparency: Just because there aren’t any physical servers to invade doesn’t mean you don’t have anything to worry about; just look at what happened with Yahoo! This problem is made even worse when you account for the lack of transparency in the cloud computing industry with respect to how and where sensitive information is stored.
- Cost management: With unpredictable workloads and pay-as-you go cloud usage, predicting your final costs may be challenging.
- IT governance: The lack of control over infrastructure operations in cloud computing makes it difficult for companies to properly manage risks, IT compliance and data quality. This is detrimental not only because the company cannot have full visibility into what’s happening with their information but also because they might be unable to make necessary changes in case something goes wrong or needs updating.
- Compliance with industry laws: When transferring data from on-premises storage into the cloud, it can be difficult to ensure compliance with industry regulations through a third party. If your organization needs to comply with legal or regulatory standards, you can learn more about compliance in Azure (Microsoft’s Cloud Services), here!
- Managing multiple clouds: Multi-cloud deployments make it difficult to address more general cloud computing challenges.
- Performance: A company is at the mercy of their provider if they are not prepared. A cloud’s performance can be unpredictable and unreliable at times (such as during outages), which could lead to a lack in productivity for an organization that relies on it too much. It’s wise to have contingency plans, so that operations remain uninterrupted.
- Cloud migration: Clouds are a lot like those tricky moving vans that just keep driving away when you think they’re about to stop. Similarly, migration projects often take longer than you’d expect and go over budget.
- Vendor lock-in: One of the most overlooked aspects of cloud computing is vendor lock-in. Switching between providers can be difficult, often due to technical incompatibilities that will result in setting up a new infrastructure for your business and incurring significant costs when moving data from one provider to another.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has certainly revolutionized the way data is stored and managed. Deploying a cloud service can help you not only cut down on IT costs but also free up your own time to focus on more important business needs!
At Mpire Solutions, we’re devoted to helping clients like you use the latest software and technology for their business. Get in touch if you’d like to learn more!
If you enjoyed this article, check out our other tech-related blog posts at https://mpiresolutions.com/blog/
Article Sources:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/samples/learn-the-basics-of-cloud/
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/cloud-platform/windows-azure-faq
https://www.verizonenterprises.com/resources/security_awareness/cloud_computing_whitepaper.pdf
http://infosecuritylabs.info/files/16584/Difference-between-Publicly-and-Privately.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing#Security
http://www.itworldcanada.com/article/cloud-security-top-concerns/?page=3
Article from: Mpire Solutions




