Everything You Need To Know About Cybersecurity

Introduction
Cyber Security is one of the most talked about topics in 2022. The reason is simple – cyber-attacks are becoming more frequent and bigger in scale. And not just from mega-corporations like Equifax and Facebook, home users also face a risk of being hacked. This guide on cybersecurity seeks to equip users with the knowledge and motivation to take steps for protecting their personal information online.
This blog post covers the following information:
What is Cybersecurity?
The Cyberthreat Scale
Expected Spending on Cybersecurity in 2022
Cybersecurity From Business Point of View
Types of Cyber Security Modules
- Critical Infrastructure Security
- Application Security
- Network Security
- Cloud Security
- Internet of Things (IoT) Security
Understanding The 3 C’s of Cybersecurity
Components Required to Create a Complete Security Posture
- People
- Processes
- Technology
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
- Malware
- SQL Injection
- Phishing
- Man-in-the-Middle
- Denial-of-Service (DoS)
Latest Cyber Threats in 2022
- Cryptojacking
- Romance Scams
- Dridex
- Cybersecurity Metrics Every Business Should Know
- Monitoring Employees
- Time to Detection (TTD)
- Time to Remediation (TTR)
- Incident Management & Reporting
- Cost Per Incident
- Average Time to Patch
Best Cyber Safety Tips in 2022
Conclusion
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the protection of computers, networks, programs, and data from theft or damage to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the same.
Cybersecurity specialists spend their days doing a variety of different things: analyzing data to identify threats, creating new security software for companies to protect their information, training employees about how to avoid cyberattacks, and working with law enforcement to investigate cybercrimes.
The Cyberthreat Scale
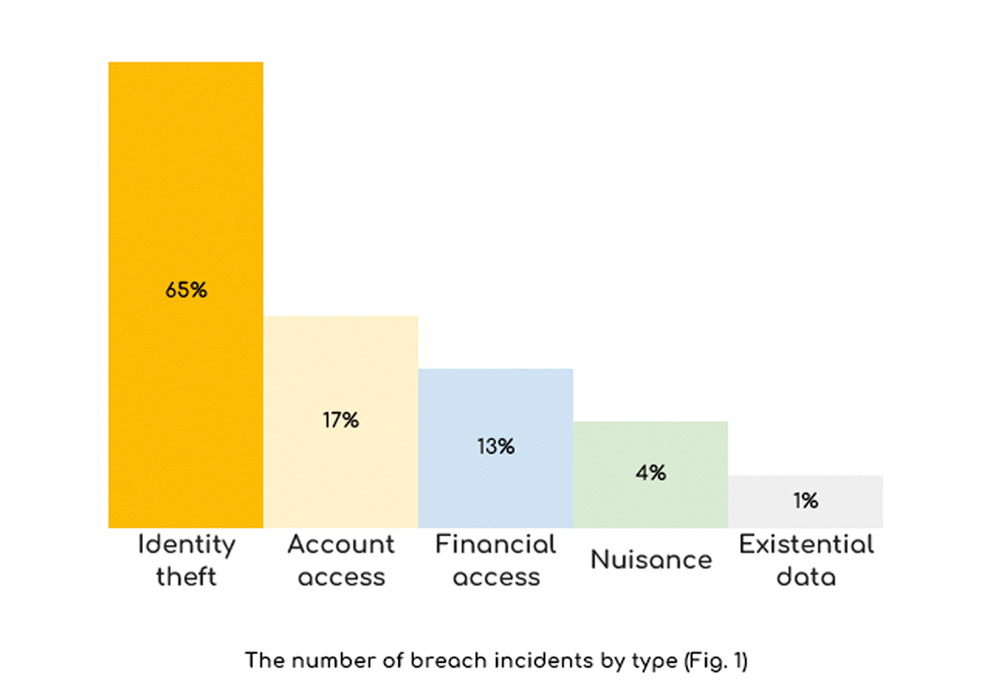
It’s a wild world out there. And it’s only getting wilder.
In 2019, the number of records exposed in data breaches is already more than double what it was in 2018. And almost the same surge applies to 2020 and 2021.
The medical field has seen an increase in cyber threats and data breaches, but so have retail locations and public entities.
Cybercriminals are still primarily interested in financial and medical records, which are then sold to other criminal organizations for further exploitation.
The threat of cybercrime is evolving at a rapid pace, and the number of records exposed in data breaches has increased significantly in this year alone. In the first 8 months of 2019, there have been 7.9 billion data records exposed due to data breaches, which is 112% more than the number of records exposed during the same period in 2018.
The most affected industries within the past year were medical services, retailers, and public entities. Medical services alone accounted for 2.7 billion records exposed or 40% of all data breach exposures to date. Retailers had 1.8 billion records exposed (26%), and government agencies accounted for 1.3 billion records exposed (20%).
According to a report compiled by security firm Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., most cybercriminals collect financial and medical data. Cybercrime is a lucrative business: financial information can be sold on the black market for tens of dollars per record; while medical information can fetch up to $300 per record.
Expected Spending on Cybersecurity in 2022
In 2022, the worldwide spending on cyber-security solutions will reach a massive $133.7 billion, the International Data Corporation predicts. This number is a full $17 billion increase from 2021’s predicted spending amount of $116.7 billion.
The report’s findings are based on a survey of more than 1,500 business and IT leaders in 10 countries and 29 industries and regions, who were asked about their planned spending over the next five years. The report also includes opinions from 500 security professionals from around the world.
International Data Corporation notes that this predicted increase is due in part to the fact that there is more money available for purchasing solutions, but also because businesses are requiring more complex defense mechanisms to protect their data and assets.
IDC believes that companies should be looking at solutions that not only provide strong protection against current threats, but also surveillance software that can catch up with emerging attacks and prevent them before they happen.
However, even with these advancements and investments, nothing can be assured about a company’s security, and there is always room for improvement when it comes to cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity From Business Point of View
Many businesspeople will describe cybersecurity as a combination of technology and risk management, but some take it one step further: they classify it as a business risk, whereas others call it a technology risk. 72% of board members classified cybersecurity as a business risk, compared to 88% who classified it as a technology risk and 12% who classified it as both a business and a technology risk.
A recent survey shows that the majority of board members feel that cybersecurity is more of a business risk than anything else. And most importantly, your chief information security officer (CISO) is held accountable for cybersecurity at 85% of organizations.
Cyber-risk incidents can have disastrous effects on businesses. Just look at Yahoo! when they were hacked in 2013, Target in 2014, or Equifax in 2017—when cyber-attacks happen, there are almost always serious consequences for the businesses involved. Organizations need to up their cybersecurity game if they want to avoid things like this from happening to them.
Types of Cyber Security Modules
There are different types of cybersecurity modules. Each type offers a way to keep data safe and should be considered when formulating a security plan. These cybersecurity modules are continuously evolving as cybercrime continues to develop as well.
Critical Infrastructure Security:
Critical infrastructure security is a broad term that refers to systems that are critical to the health and wellbeing of a community and/or country. These systems often have a huge impact on the daily lives of people and are fundamental to the functioning of a society as a whole. For example, water and power systems keep people alive, transportation systems allow people to get around, and communications systems allow for the flow of information. Critical infrastructure security is essential to keep these systems safe from deliberate or unintended harm.
Application Security:
Application security focuses on securing applications that are used by an organization and its employees. Applications are in use every day, throughout an organization, and even on employee devices. This application-based approach to cybersecurity means that it needs to be a top priority for any employer.
Application security, just like other forms of cybersecurity, is focused on the protection of applications from various threats. These threats can be from individuals or from malicious software (malware), both of which can infiltrate an organization and cause devastating damage to the company or its employees.
This type of security focuses on securing access to applications, securing data within those applications, ensuring integrity within those applications, and ensuring that the application does not have any manipulation issues (i.e., using application proxies). The main purpose of application security is to ensure that what you are seeing in your application matches what is actually in storage behind the scenes.
Network Security:
Network security is a broad category that can be broken down into subcategories. First, network security deals with protecting computers, networks, and the data transmitted across networks. It also encompasses firewalls, routers, and other devices used to regulate the flow of information from one place to another. Finally, network security covers internet-based threats like malware, viruses, Trojans, and ransomware.
Network security has two main components: network attack and network defense.
Network attack is all about accessing a company’s data and systems by breaking into them. It also includes penetration testing (also called ethical hacking). A penetration test is a simulated attack on a network’s security that allows an organization to find out how well its defenses are working. Penetration tests are performed both by outside companies using special software and by the organization itself using in-house employees.
Network defense is all about preventing unauthorized access to a company’s data and systems. Network defense includes preventing the spread of viruses and other malicious programs, protecting networks against denial-of-service attacks, and designing employee policies to prevent social engineering.
Cloud Security:
Cloud security is one of the most rapidly growing types of cybersecurity. Cloud computing is a method of storing data, software, and running applications in a hosted environment instead of on one’s own computer or property. This allows users to collaborate and share information in real-time, while the cloud hosting service takes care of the maintenance and security of the system.
Cloud security is generally managed by a third party that offers certain perks to users for their business. These services generally include secure storage and access management, customized reporting, and maybe even an SLA (Service Level Agreement).
Internet of Things (IoT) Security:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an umbrella term for the network of physical objects connected to the internet, which can communicate with each other and with their users. The IoT includes all sorts of devices: smart thermostats, appliances, wearables, smart refrigerators, and many more.
The IoT has been a catalyst for the development of new cybersecurity challenges because these devices are often very low priced and lack standardization in design as well as security mechanisms. Some IoT devices are nothing more than a simple microprocessor connected to the internet, while others may contain memory storage and battery or solar power. The potential attack surface is huge and attackers can use a variety of methods to exploit these devices.
Understanding The 3 C’s of Cybersecurity
Cybercrime, cyberattack, and cyberterrorism are attacks on a network. When we hear the phrase, “cyberattack,” it makes us think of an attack on our computer. But, some attacks are against a network. A cyberthreat is an attack via a traditional Trojan virus or spam. Cybercrime and cyberterrorism target individuals and groups as well. So, what is the difference between these cyberattacks?
✔ Cybercrime means illegal activity through the internet—such as stealing money from bank accounts, operating illegal gambling sites, or sharing pornography.
✔ Cyberattack involves an individual or organization tampering with the system of another individual or organization through the internet. This can include threatening to publish information about someone or something if they don’t pay a ransom.
✔ Cyberterrorism involves an attack by a group or nation-state against an organization for political reasons. This could include threatening to publish information about a company if they don’t pay a ransom, which is similar to a cyberattack except it is done by a group rather than an individual.
Components Required to Create a Complete Security Posture
“The old saying, ‘All you need is antivirus software’ has been propagated for so long that it seems to be commonly accepted as the Holy Grail of securing your network. The network security posture should be a defense-in-depth strategy consisting of multiple layers and segments.”
Until this day, the discipline of information security has many challenges, and failures continue to happen. One of these challenges is the failure of organizations to securely protect their operations and assets. This concern is what drives information security professionals to create more effective strategies, alongside with development and implementation of different ways in securing the organization’s data from threats coming from any direction.
People:
Many companies believe that cybersecurity is only a technical issue, but this is not true. Cybersecurity is a people problem. People are the most important component in a cybersecurity posture. The reason for this is simple: people, who understand the technology and know what they’re doing, can affect the entire environment’s security posture.
These three steps are necessary to properly secure your company’s network:
1). Hire employees who understand the importance of cybersecurity and have experience working with technology. These people will be able to help with your security issues before they become dangerous.
2). Make sure your employees are trained on the proper way to use technology in your office, like computers or smartphones. You don’t want them accidentally deleting important files or sending sensitive information to the wrong place.
3). Encourage employees to make cybersecurity a priority in their daily lives, both at work and outside of work (at home or when out with friends). The best way to do this is by setting an example for them and ensuring that everyone understands how important cyber security is for everyone’s safety and privacy, not just the company’s protection from outside hackers and attackers.
Processes:
Cyber threats are a serious business, and they’ve been on the rise. Organizations need to ensure that they have the right processes in place to manage risk on an ongoing basis.
The success of a cybersecurity program depends on how well it can adapt to changes in the environment, including new threats and technologies. This can be done through effective processes for monitoring the organization’s cybersecurity posture and adapting to changes. “Monitoring” means determining whether or not the organization is achieving its goals for its cybersecurity program, including improving cybersecurity measures over time and ensuring business objectives are met. “Adapting” refers to making changes in response to events or conditions that affect or may affect the organization’s cybersecurity posture.
In addition, processes should exist to help ensure compliance with applicable laws, regulations, standards, and policies; identify gaps in security coverage; prioritize funding and resources; continuously develop security expertise; assign roles and responsibilities; address staff turnover; monitor and assess risks; determine appropriate controls; evaluate effectiveness.
We reached out to a cybersecurity expert with MpireSolutions, and asked him if he could share any advice for other companies looking to stay safe.
“Cybersecurity,” said the agent, “starts with people.” He noted that many cybersecurity professionals focus too much on technology while not giving enough attention to people and processes. Management should make sure that employees understand how breaches happen and the role they play in preventing them. This can be done through training programs and regular meetings with managers.
The second thing management should do is create clear lines of responsibility. This means that each employee knows what their organization’s policies are for dealing with cybersecurity threats, as well as how to report breaches or attempted breaches. The human element can’t be ignored when it comes to security.”
Technology:
When it comes to cybersecurity, there is no silver bullet. But according to a study, technology plays an active role in any successful security posture and can provide distinct advantages for an organization looking to ward off cyber threats.
A modern enterprise is only as strong as its weakest link, which may explain why most breaches start with a simple phishing email. Even in the face of constant attacks, experts agree that technology is the key to mitigating damage.
Businesses that are not fully aware of their IT vulnerabilities are at high risk of getting breached; this becomes especially true if they don’t have a strategy in place to be able to recover quickly.
Cybersecurity has become a top priority for companies worldwide, and it’s not going away anytime soon. Organizations must continue to invest in their defense mechanisms so that they can take advantage of new technologies before attackers do.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats are something we hear and read about all the time. New reports come out daily that detail the latest cyber intrusion, data breach, or hack that resulted in a company losing their sensitive personal information or suffering some sort of loss because of a security vulnerability. Cybersecurity threats can take many forms and we won’t attempt to cover them all here. However, there are 5 basic types of cybersecurity threats you need to be aware of:
Malware
Malware is short for “malicious software,” and it refers to any type of software that is intended to cause harm to computer systems or the data stored on them. Malware can be used for a number of different purposes, including:
- Intentional destruction of data
- Hijacking a user’s computer to steal his or her account login information
- Controlling the user’s computer for use in launching attacks against other systems
Malware is often installed by tricking users into downloading and executing it, but some forms of malware are capable of infecting computers even when they’re not downloaded onto them.
SQL Injection
SQL injection is a type of attack that exploits a security weakness in an application that uses Structured Query Language (SQL) databases. SQL injections are possible because an application does not validate input from the user before using it in an SQL query. The attacker takes advantage of this by inserting code into the SQL query to be executed on the database server, which can then be used to reveal information from the database or even take control of the server itself.
Phishing
Phishing is the practice of sending fraudulent emails in an attempt to collect sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details (and sometimes indirectly stealing money from a victim’s bank account). The term is a neologism created as a homophone of fishing due to the similarity of using bait in an attempt to catch a victim. Phishing is usually carried out by email spoofing or instant messaging, and it often directs users to enter details at a fake website whose look and feel are almost identical to the legitimate one. Phishing emails may contain links to websites that are infected with malware (which will infect the user’s computer), or sites where users are asked to supply personal information, such as passwords.
Man-in-the-Middle
A man-in-the-middle attack is a method used by cybercriminals and malicious hackers to obtain sensitive information from their victims. It involves an attacker placing themselves between two separate parties in a conversation, pretending to be both participants. This is done by intercepting data sent between the two parties and duplicating it before sending it to each party. The attacker can monitor the responses of each of the parties to replicate the correct responses.
To prevent being a victim of this type of attack, users should verify that the address bar on their web browser begins with “HTTPS://” instead of HTTP://”. This indicates that the website is using a secure connection. If this is not present, then it’s possible that the user is being connected to a fake site controlled by the attacker.
Denial-of-Service (DoS)
A denial-of-service attack (DoS attack for short) is a type of cyberattack that is used to deny users access to resources or systems. It is considered one of the most primitive types of attacks, though it can prove just as effective as more advanced methods. A successful DoS attack shuts down a system or server by overloading it with massive amounts of traffic, preventing legitimate traffic from accessing the resource.
DoS attacks are commonly performed using one or more computers that have been compromised via malware such as a Trojan horse, worms, or viruses. The compromised computer or computers then send requests to the target website to overload its servers and either shut it down completely or significantly slow it down until normal operations cease. The attacker can use their own computer or enlist their friends and family’s computers, which is why some DoS attacks are also called distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Latest Cyber Threats in 2022
Cyber attacks in the coming year will be more sophisticated, more damaging, and much harder to predict than ever before. Our lives are now almost completely dependent on various types of information and communication technology, which makes us vulnerable targets.
The world threat level is not going down. It’s rising. There are a number of cyber threats that you need to be aware of. Let’s take a closer look at just a few of the various threats that are likely to pop up on your radar moving forward.
Cryptojacking
Crypto Jacking is the practice of using someone else’s computer without their permission to mine cryptocurrency coins, often for someone else’s financial gain.
Cryptojacking comes in several forms, but what they all have in common is that the victim does not give consent for an application to use their computing power to mine cryptocurrency. Some cryptojacking software is installed by an individual on a device they own. Other times, cryptojacking software is installed by cybercriminals who target vulnerable computers and devices. Devices that can be targeted for cryptojacking include computers, phones, tablets, smart TVs, and even smart fridges!
Cryptojacking can be done in the background while users continue to work on their infected devices. Although it doesn’t change any settings or affect the performance of a device and can be difficult to detect, it can slow down a device since mining requires a lot of processing power.
Cryptojackers may use other malicious software that also secretly uses the victim’s computer and network resources, including crypto-miners or ransomware programs. Therefore, it is important to keep your operating systems up-to-date and make sure you are protected with security software.
Romance Scams
Romance scams are fake online relationships used to swindle people out of money and items. Scammers prey on lonely people looking for companionship, taking advantage of their loneliness, loneliness, and optimism. These scammers create fake profiles on dating sites, social media platforms, chat rooms, and more. They pretend they’re a potential partner, eventually asking the victim to send money or other items. They often claim they need money to help them come to visit the victim. If they’re successful in scamming someone out of money/items, they move on to a new victim as quickly as possible. Romance scams are especially hard to identify because many real people use these sites as well and it’s hard to tell when someone is pretending to be someone they aren’t.
Dridex
Dridex is a type of malware that was first discovered in 2014. But has become widespread in 2022. It’s a Trojan horse, meaning once it infects your computer, it steals information from you and sends it to cybercriminals. It enables criminals to steal passwords and banking information and then use it to access your bank accounts. The main goal behind the creation of Dridex was to make money, which makes it an example of economic espionage rather than traditional state-sponsored hacking.
Cybersecurity Metrics Every Business Should Know
One of the biggest security risks your business may be facing are the ones you didn’t even know about — and for that, it’s important to regularly review your security metrics.
Did you know that over 1.33 million cyber attacks are blocked by different cybersecurity firms every month? That’s the equivalent of over 6,200 attacks every hour. It is essential to empower your business to move away from the default settings and enable necessary tools to achieve greater visibility and better control over your data, devices, and applications.
Monitoring Employees
Monitoring employee behavior is an important metric for an organization to track so that its cybersecurity can be evaluated. Monitoring employee behavior allows an organization to assess its employee’s ability to identify and report security incidents, as well as their understanding of how to report a data breach effectively.
When it comes to cybersecurity, many companies focus either on the technology or processes being used by the business but fail to consider whether their employees are even aware of these processes and technology. This can cause issues if employees lack the knowledge necessary to prevent cyberattacks, or if they don’t know the right steps to take in a data breach situation.
Monitoring employee behavior includes:
– Assessing the employee’s level of awareness of organizational policies
– Examining the employee’s ability to identify cybersecurity risks
– Evaluating an employee’s response time when identifying cybersecurity risks or breaches
Time to Detection (TTD)
Time to detection (TTD) is an important cybersecurity metric for a business; it measures how long it takes a business to detect cyber threats. The TTD metric is calculated by dividing the time between the first and the last cyber threat attack against a business into the total number of attacks that occur over a given time period. The metric allows businesses to measure their cybersecurity preparedness.
Time to Remediation (TTR)
Time to remediation is an important cybersecurity metric for business. It is a measure of how long it takes to remediate a threat or incident from the point it is detected and reported. Although the time it takes to perform a public disclosure after detecting a threat or incident is also important, Time to Remediation focuses on the time between threat detection and an operational solution being put into place.
Incident Management & Reporting
Incident management and reporting are important components of a strong cybersecurity strategy. Incident management can help determine the scope and impact of an attack, while incident reporting must be accurate and comply with regulatory requirements. Incident reporting and data analysis can also help identify trends in attack patterns to allow for timely responses to new threats. Accurate incident reporting helps businesses to maintain compliance with industry regulations, as well as legal obligations to their customers and partners.
Cost Per Incident
Although the importance of cybersecurity metrics is clear, it can be difficult to determine which metrics are most important. Many metrics exist, and understanding how they relate to one another is a crucial part of evaluating security practices. One important metric is Cost per Incident, which calculates the cost of an incident in relation to the organization’s revenue. This metric can help determine whether the organization has sufficient resources in place to protect data and assets.
This metric can be derived by dividing total costs by the number of incidents recorded and viewing the result as a percentage. For example, if a business has 50 incidents over a given period and spends $10,000 on related expenses, it’s [Cost per incident] would equal $200.
Average Time to Patch
The average time to patch is an important Cybersecurity Metric for a business. A company’s data is the most valuable asset it has, and protecting that data from cyber-attacks is vital to its success. The longer it takes to patch a vulnerability in a computer program, the greater the risk that someone will exploit that vulnerability. The more frequently a company patches its vulnerabilities, the lower the risk of cyber-attack.
Best Cyber Safety Tips in 2022
With the rise of technology, our lives have changed in many ways. One of the most important is what we do online. The internet is a powerful tool that can connect people across the world, but it also comes with risks. In recent years, cybercrime has increased dramatically. You can protect yourself and your loved ones from cyber attacks by following some simple steps:
Update your software and operating system security patches regularly. Make sure you are not running old software versions or out-of-date operating systems that might be vulnerable to hacking attacks.
Use anti-virus software on your devices to help protect them from malware and viruses. Make sure that you keep this software up to date and fully functional on all your computers and mobile devices.
Use strong passwords for all of your accounts and change them frequently. Change default passwords for any installed software. Password managers like 1Password and LastPass are great resources for creating unique, complex passwords for all of your accounts, though they do require some initial setup time to use effectively.
Do not open email attachments from unknown senders or download files from unfamiliar websites. Cybercriminals often send out emails or host links to infected files embedded in websites designed to steal personal information or infect devices with malware when you click on the link inside the email.
Avoid public WiFi. Hackers are often using WiFi networks in public places to hack into private accounts. To protect yourself and your information, it is a good idea to only use secure WiFi networks.
Conclusion
One of the biggest challenges for organizations today is understanding the scale and scope of cybersecurity vulnerabilities, as well as identifying and prioritizing cybersecurity threats. In addition, with an increasingly complex attack environment, it is more important than ever to have a centralized view of both your digital assets and your exposure to cybersecurity threats.




